A sore throat is a painful but common affliction that everyone suffers from on occasion. It may be the first sign of a cold, the result of strained vocal cords or a symptom of a more serious condition such as strep throat. As miserable as a sore throat can make you feel, in many cases symptoms clear up quickly and without medical treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of a Sore Throat?
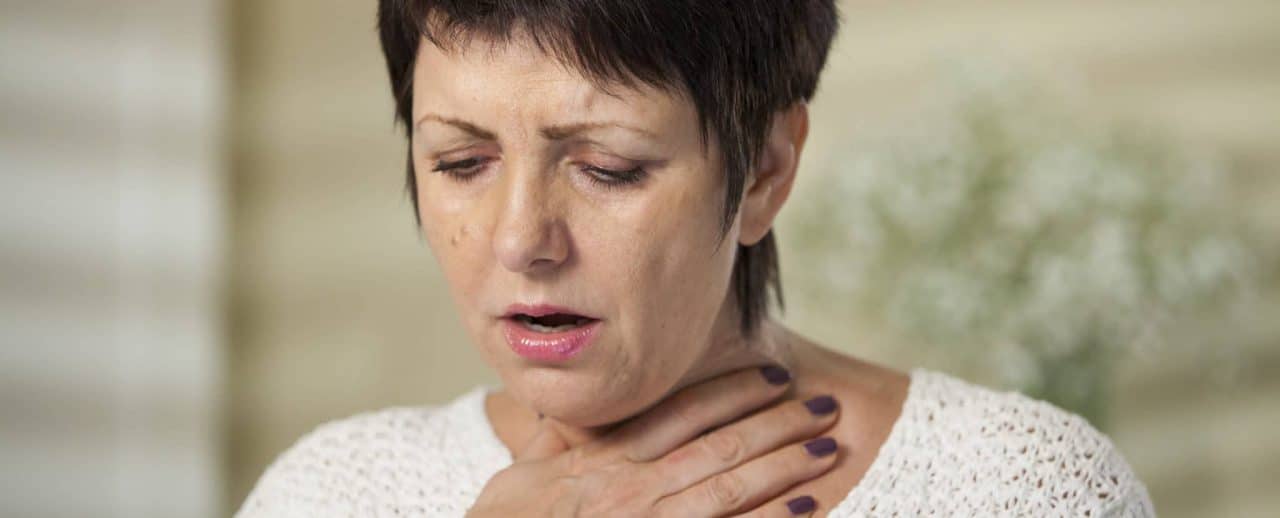
Symptoms of a sore throat include pain, scratchiness, dry throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, swollen neck or jaw glands and swollen or inflamed tonsils. You may also have a fever, chills, cough, runny nose, sneezing, headache, muscle and joint aches, nausea and vomiting.
What Causes a Sore Throat?
Most sore throats are the result of viral infections, often related to the common cold or flu. Bacterial infections can also lead to sore throats. Some of the more common ones include strep throat, tonsillitis, whooping cough and diphtheria.
Additional factors that can cause a sore throat include allergies, acid reflux, environmental irritants, dry air and strained vocal cords. Occasionally a more serious condition, such as a tumor or HIV, can cause a sore throat.
Hoarseness is an inflammation of the larynx that results in a change in the voice, making it sound breathy, raspy, scratchy or strained. There may be changes in volume and pitch, as well. Hoarseness falls under the medical category of dysphonia, which refers to voice impairment or any sort of difficulty speaking.
What Causes Hoarseness?
Hoarseness is the result of a problem with the vocal cords. It can be caused by a variety of different conditions including cold or sinus infections, acute laryngitis, voice misuse or abuse, benign vocal cord lesions, acid reflux, vocal hemorrhage, tobacco and alcohol use, thyroid diseases, cancer, trauma to the voice box and neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s or spasmodic dysphonia, a chronic vocal cord disorder.
Chronic Cough
A chronic cough is defined as one that lasts eight weeks or longer. More than simply an annoyance, a lingering cough can disrupt your sleep and affect your work. It may be accompanied by other symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, runny nose, congestion and heartburn.
If you have a persistent cough that doesn’t disappear after a reasonable amount of time, make an appointment with your physician for an evaluation.
What Causes Chronic Cough?
A cough is your body’s way of expelling a substance that is irritating the air passages. When cells lining the air passages become irritated, they trigger air in the lungs to be forced out under high pressure.
Chronic coughing can be triggered by a variety of factors. These include:
- Postnasal drip.
- Asthma.
- Allergies.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Upper respiratory tract infections.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (includes bronchitis and emphysema).
- Pertussis (whooping cough).
- Air pollution.
- ACE inhibitors (found in some medications used to treat high blood pressure and heart disease).
Smokers are most at risk for developing a chronic cough, as are those exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke.
What Are the Symptoms of Chronic Cough?
You should contact your doctor if your cough is accompanied by fever, excessive phlegm production or blood; fails to improve after your other symptoms have disappeared; interferes with your daily activities or sleep; or you have difficulty breathing.
Treatment & Prevention
Home remedies are often the most effective treatment method for a sore throat. Try gargling with warm salt water periodically through the day. Make sure you drink plenty of liquids, and use throat lozenges and cough drops to relieve soreness and irritation.
A humidifier is often helpful. Over-the-counter pain relievers and decongestants are beneficial at providing relief as well. If your sore throat is caused by a bacterial infection, you’ll need to treat it with antibiotics.
There are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing a sore throat in the future. Practice good hygiene by washing your hands frequently with warm water and soap, cough or sneeze into a tissue or your sleeve and do not share food or utensils with others who are sick.
Call Willamette ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery at (503) 581-1567 for more information or to schedule an appointment.
“Have always found the staff and doctors here to be helpful. This was my first visit with Dr. Prze after Dr. Allan retired, and he was very friendly, enthusiastic, and thorough. It was obvious he had read my chart carefully before my checkup.”